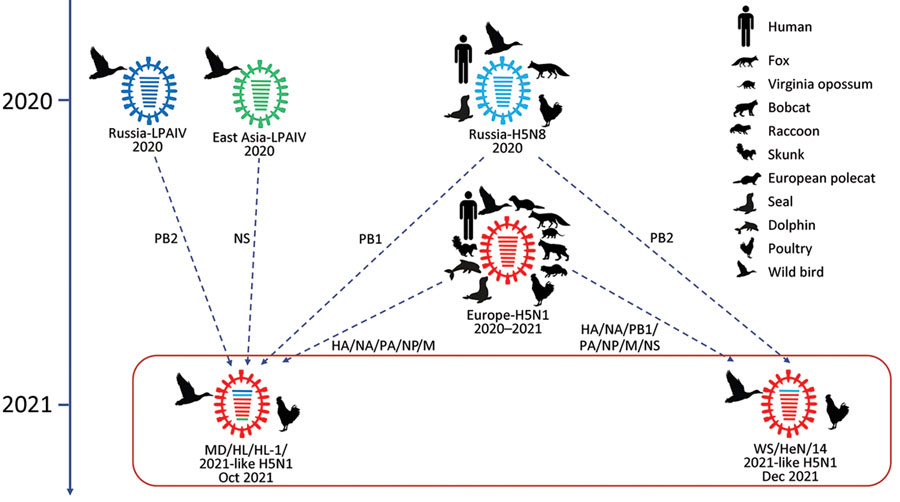
As the H5N1 pandemic looms, its severity and potential impact demand immediate attention. This virus has emerged as a global threat, posing significant risks to public health and the economy.
Understanding the nature, transmission, and consequences of the H5N1 virus is crucial for effective preparedness and response measures.
Overview of H5N1 Pandemic
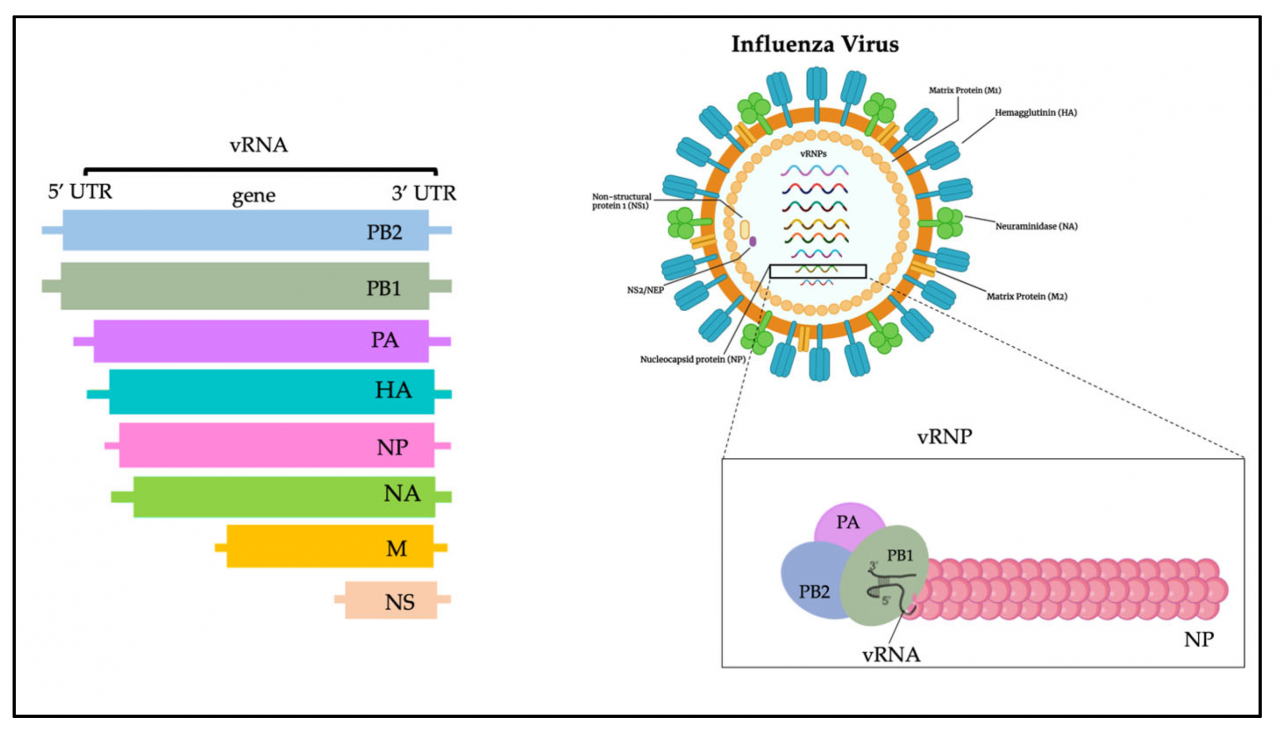
The H5N1 virus is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that has caused significant concern due to its potential to cause severe illness and even death in humans. It is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds, but can occasionally jump to other species, including humans.
The virus has been responsible for sporadic outbreaks in humans, primarily in Asia and Africa, with varying degrees of severity.
Historically, H5N1 outbreaks have occurred in poultry, leading to mass culling of infected birds to prevent further spread. However, in some cases, the virus has crossed the species barrier and infected humans, causing a range of symptoms from mild respiratory illness to severe pneumonia and organ failure.
Transmission and Symptoms
H5N1 is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, such as feces or saliva. Humans can become infected by handling infected poultry, inhaling airborne virus particles, or consuming contaminated food products, such as undercooked poultry meat or eggs.
The incubation period for H5N1 infection is typically 2-7 days, although it can range from 1 to 10 days. Symptoms of H5N1 infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Mild cases may present with flu-like symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches.
In more severe cases, H5N1 can lead to pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, and multi-organ failure.
High-risk groups for severe H5N1 infection include individuals with underlying health conditions, such as chronic respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. Factors contributing to severe illness include the amount of virus exposure, the strain of the virus, and the overall health of the infected individual.
Public Health Measures
Public health measures are crucial to prevent and control the spread of H5N1. Preventive measures include avoiding contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, practicing good hygiene, and consuming poultry products that have been properly cooked. Surveillance and monitoring systems are essential for early detection and containment of H5N1 outbreaks in poultry populations.
In healthcare settings, infection control measures, such as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper hand hygiene, are critical to prevent transmission of H5N1 from infected patients to healthcare workers and other individuals.
Impact and Management, H5n1 pandemic
H5N1 outbreaks can have significant economic and societal impacts. Mass culling of infected poultry can disrupt the poultry industry and lead to economic losses. Outbreaks in humans can strain healthcare systems and cause widespread fear and anxiety.
International collaboration is essential for pandemic preparedness and response. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other international organizations play a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to monitor H5N1 outbreaks, develop vaccines and antiviral therapies, and provide technical assistance to affected countries.
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) | Neuraminidase inhibitor | Reduces viral replication | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Zanamivir (Relenza) | Neuraminidase inhibitor | Reduces viral replication | Bronchospasm, nasal irritation |
| Peramivir (Rapivab) | Neuraminidase inhibitor | Reduces viral replication | Headache, diarrhea |
Research and Development
Ongoing research efforts are focused on understanding H5N1 transmission, pathogenesis, and vaccine development. Scientists are working to identify potential vaccine candidates and antiviral therapies that can effectively prevent and treat H5N1 infection. Surveillance and monitoring systems are also being improved to track viral evolution and resistance.
Communication and Education
Effective public communication is crucial during an H5N1 pandemic. Clear and accurate information dissemination can help reduce fear and anxiety, promote preventive behaviors, and encourage vaccination. Public health campaigns should focus on educating the public about the risks of H5N1, preventive measures, and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms develop.
Ultimate Conclusion: H5n1 Pandemic
The H5N1 pandemic is a pressing challenge that requires a coordinated global response. By implementing robust public health measures, fostering international collaboration, and investing in research and development, we can mitigate the impact of this virus and protect the health and well-being of our communities.